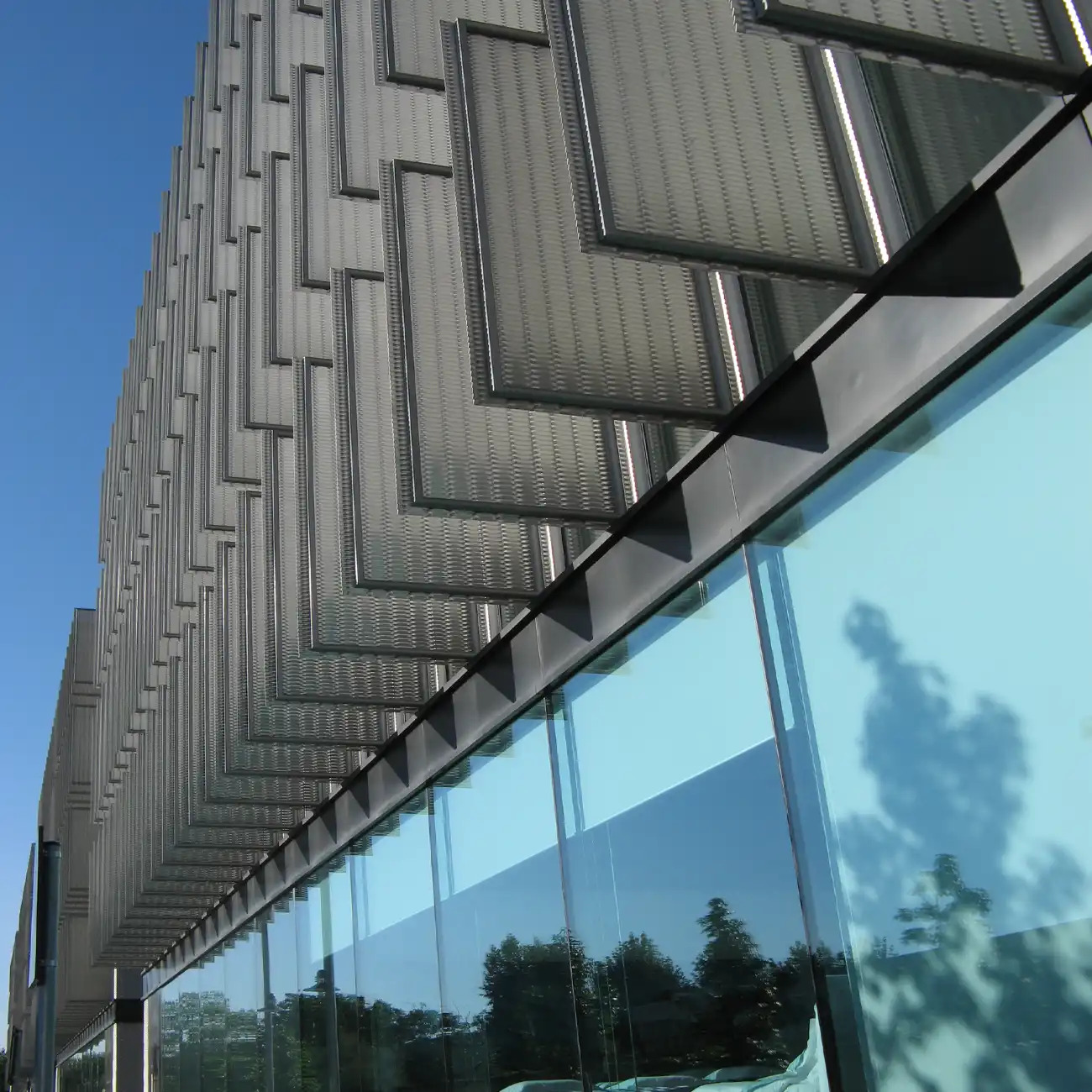
3D Simulation of Shutter Control with Dynamic Sun Path and Shadow Projection
3D Simulation of Shutter Control with Dynamic Sun Path and Shadow Projection
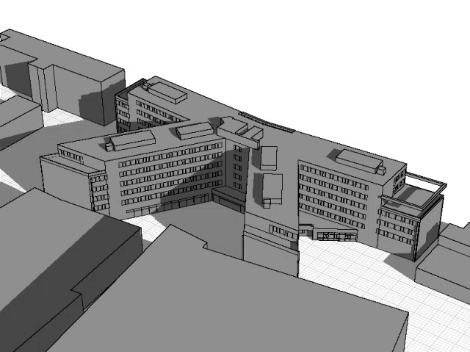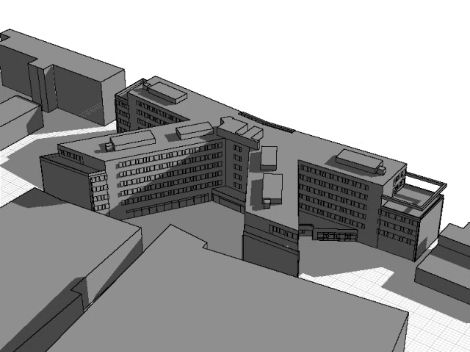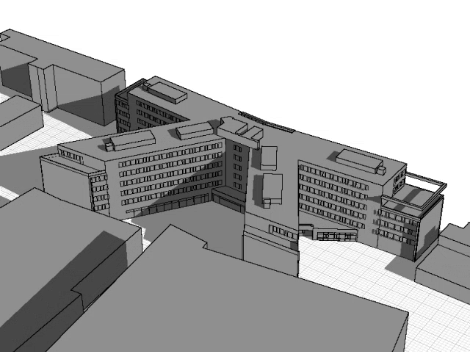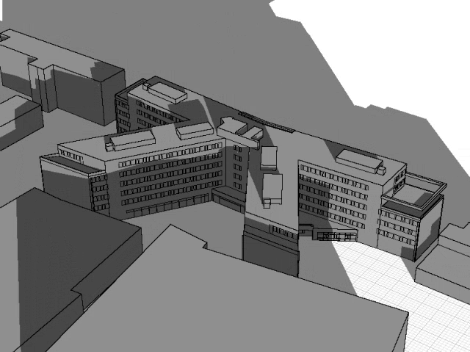
The simulation integrates building geometry and surroundings to visualize dynamic shading and sun angles across the day or year. This aids in optimizing shading control for improved energy efficiency and indoor comfort.
Functions
Functions
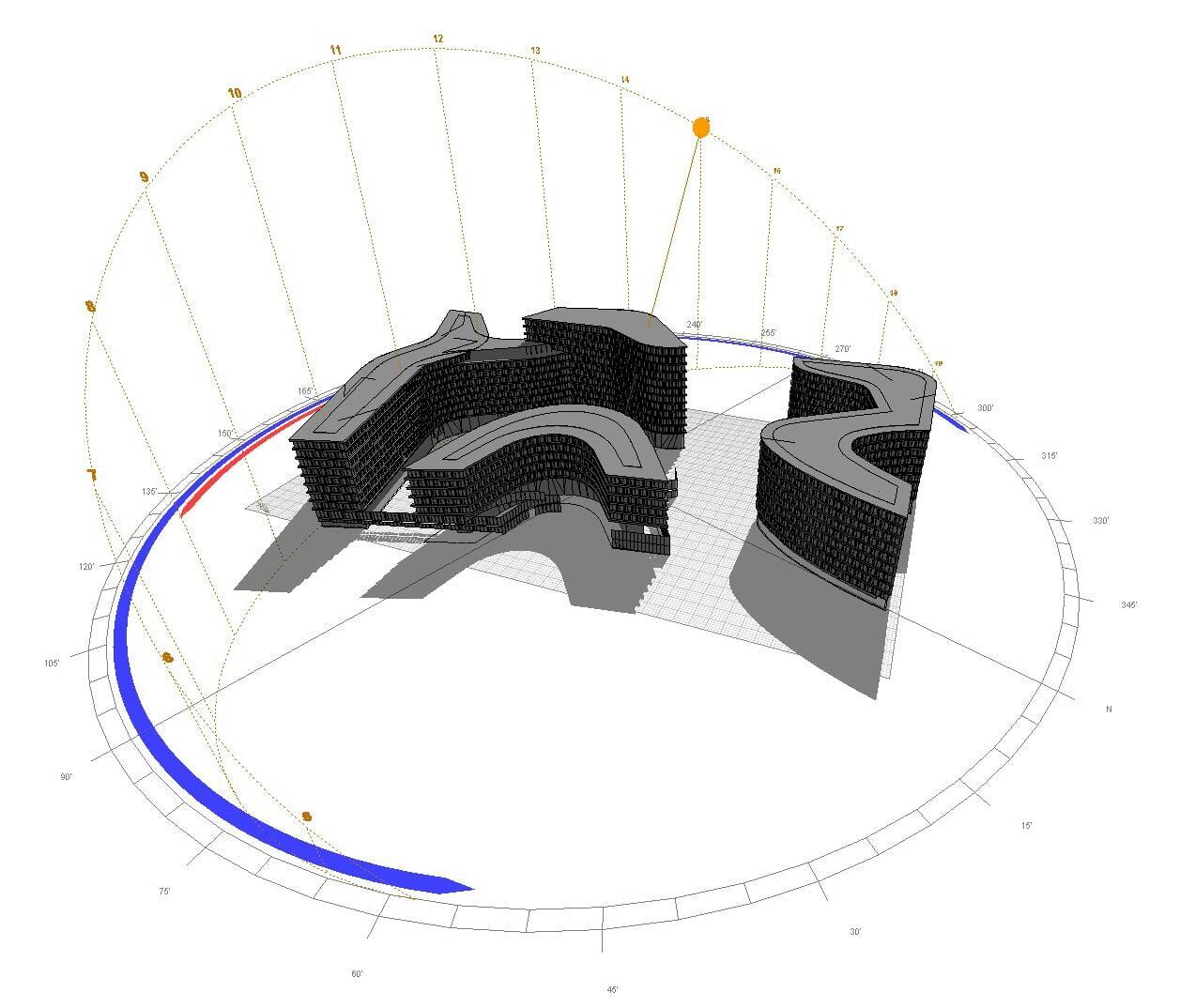
A 3D model of the building and surrounding objects is created to precisely simulate shadow paths and optimize the shading control.
Based on simulations and real-time weather data, the blinds and slat positions are automatically controlled.
Blinds can be controlled individually or in groups, depending on the need.

In addition to automation, manual control is available, allowing customization to specific project requirements.
Adjustable brightness and hysteresis thresholds are available depending on the sun’s position, helping to prevent glare.
The slat positions are automatically adjusted according to the sun's position to create optimal lighting conditions.
Thousands of blinds can be centrally managed and visualized.
Advanced Geometric Modeling for Precision Shading

3D-Volume Model
A 3D-volume model provides a detailed representation of building geometry, enabling precise calculations for shading, sun paths, and shadow projections to optimize energy efficiency and indoor comfort.
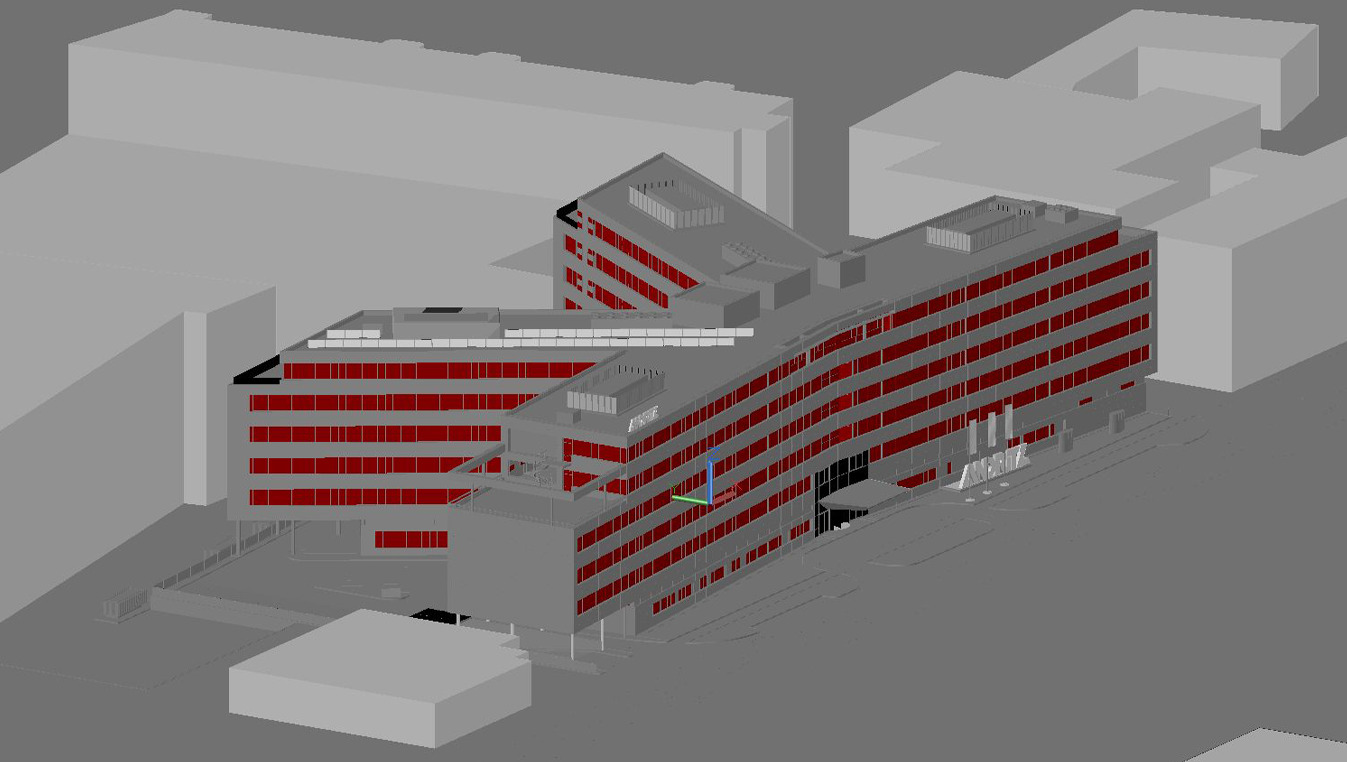
Grid Model
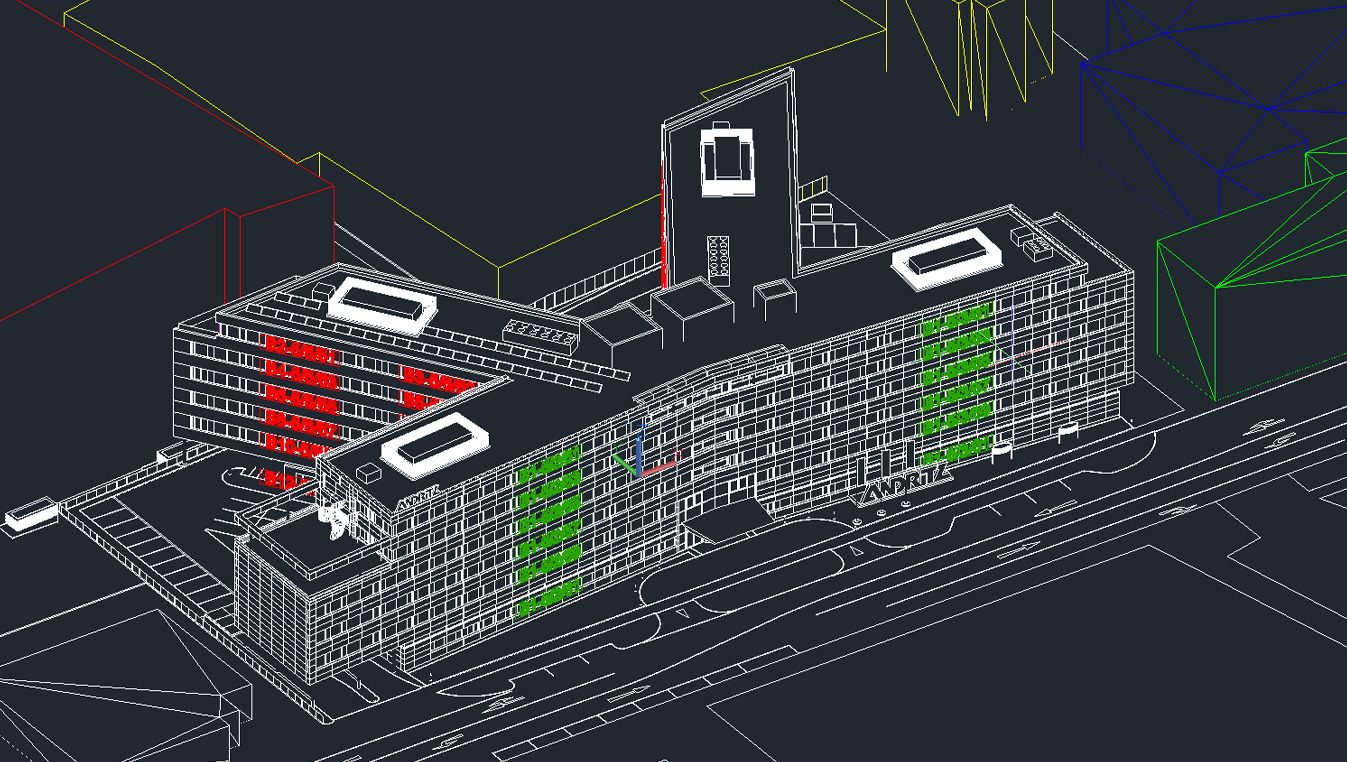
A grid model divides the building surface into segments, enabling precise analysis of shading, sunlight distribution, and shadow patterns for optimized control of blinds and energy efficiency.
Window Grid Model
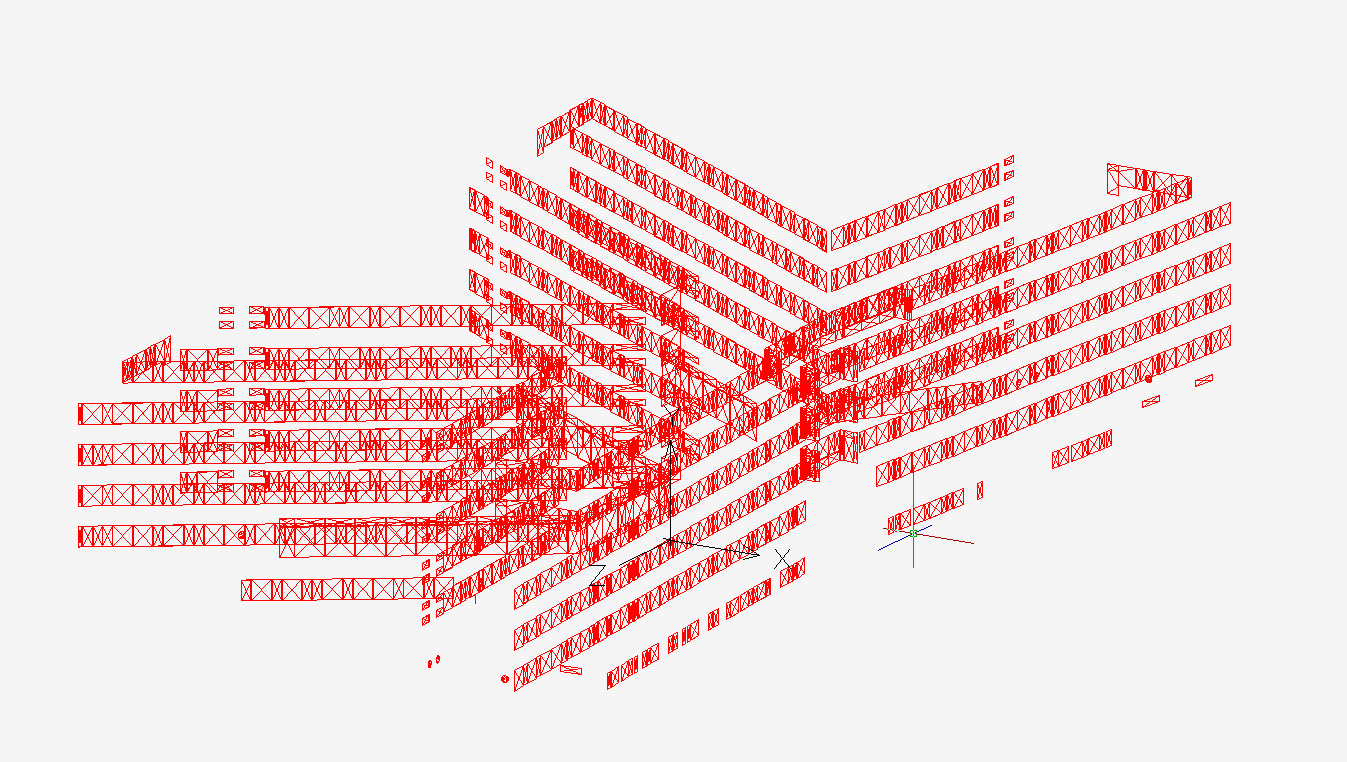
The window grid model divides window surfaces into smaller segments, allowing detailed analysis of sunlight exposure, shading, and shadow dynamics to optimize blind positioning.
 Shutter Control App
Shutter Control App
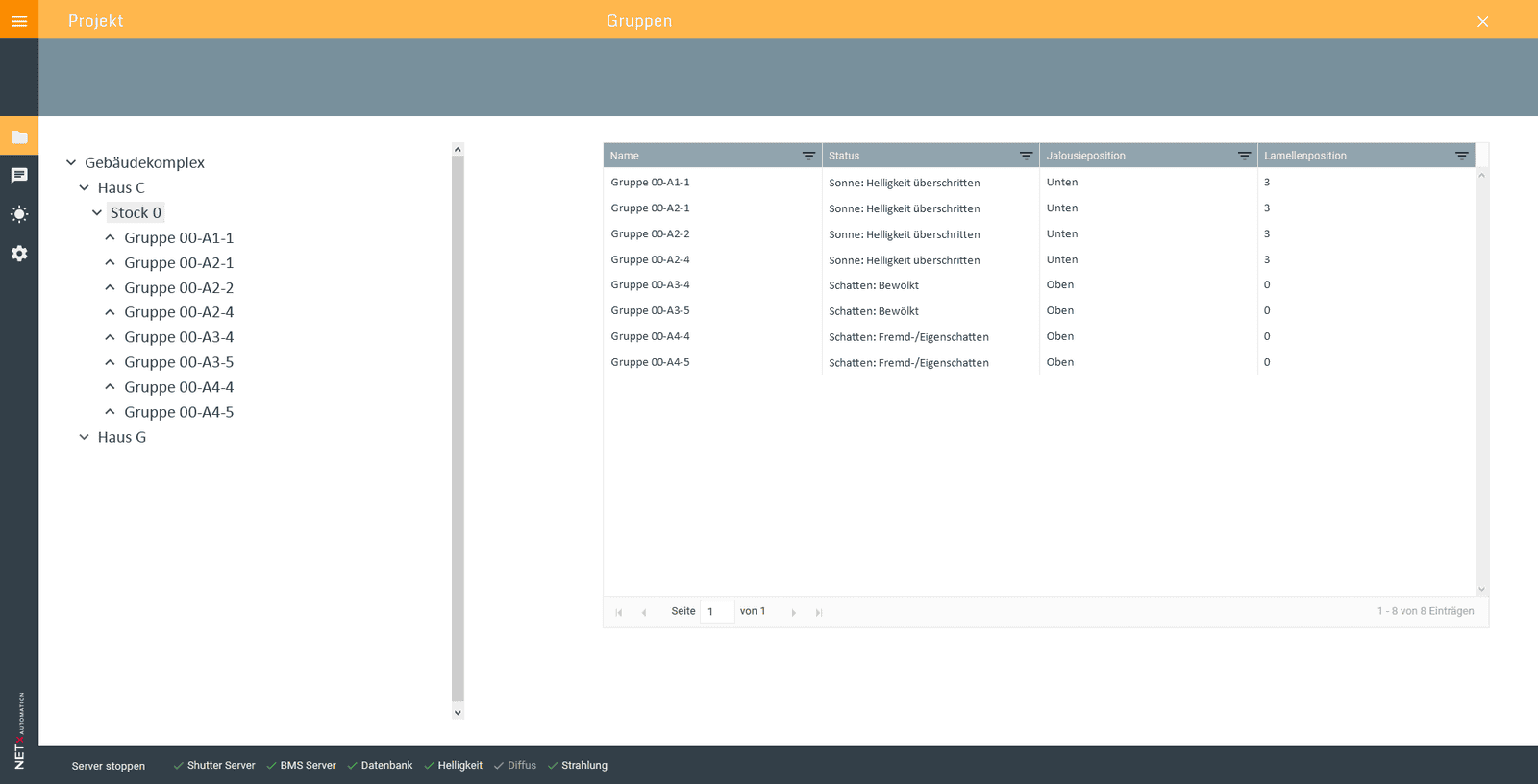
The Shutter Control App is accessible through the Web Manager of the NETx BMS Platform. It is used to configure and control the Shutter Control Module.
Functions
Functions
Automated Control
- Based on 3D simulations of the sun’s trajectory and weather station data.
- Lamella adjustment based on azimuth and elevation angles of the sun.
- Optimization of the incidence angle to minimize direct sunlight.
- Adaptation to shadows cast by surrounding buildings.
Weather-Dependent Control
- Integration of primary and secondary weather stations to ensure data availability.
- Dynamic adjustment to diffuse light conditions and protection through wind alarms.
- Monitoring of brightness, temperature, and other climatic conditions.
Scheduler
- Time-based events to temporarily override automated positions.
- Repeatable events (daily, weekly, monthly).
- Integration of Scheduler XCommands for complex control tasks.
Manual Override
- Manual control of individual blinds by the user.
- Configurable time intervals for returning to automated control.
Grouping and Hierarchy
- Organization of blinds into automatic groups and zones (e.g., floors, facades).
- Dynamic adjustment and management through Excel files.
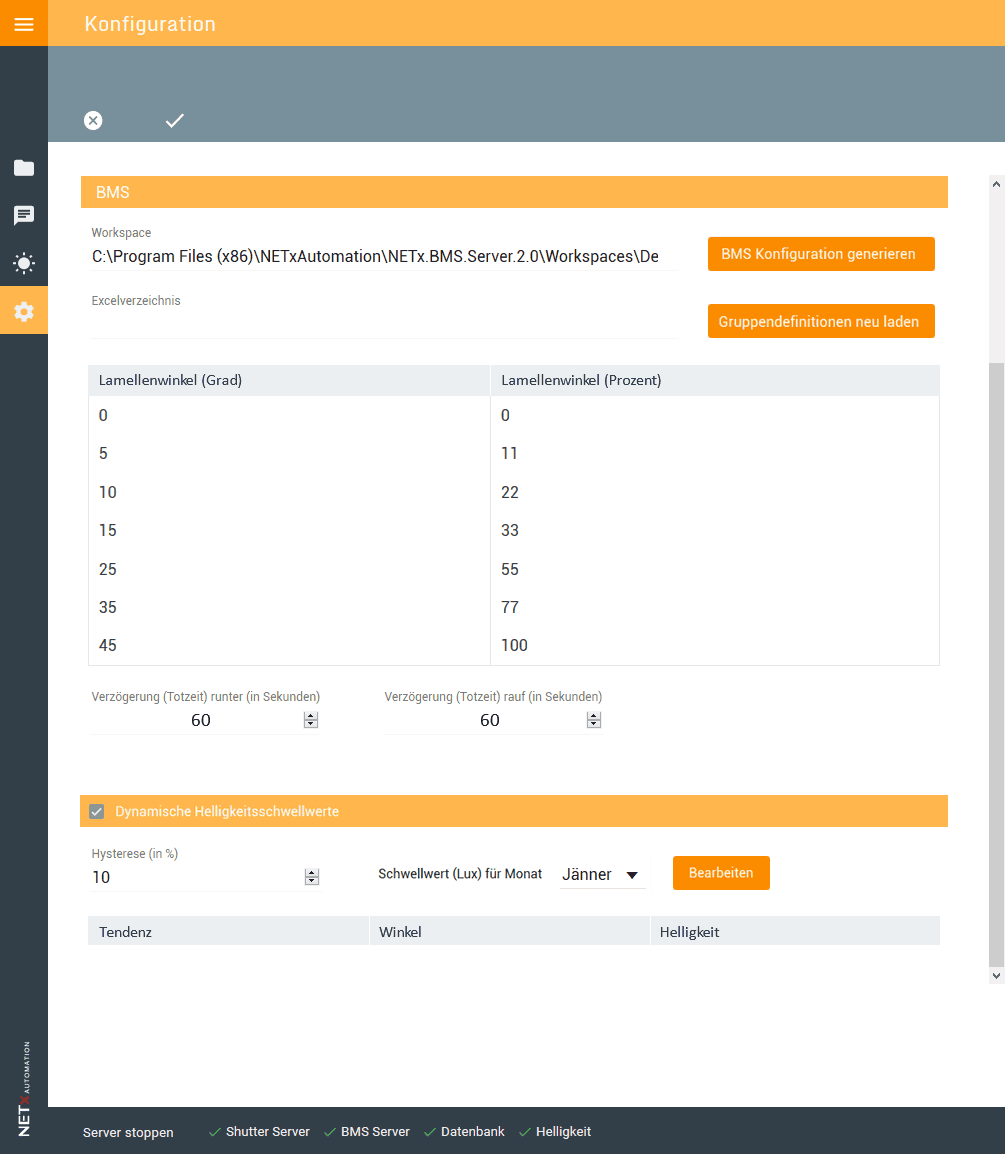
Configuration
- Import of project and configuration data from Excel files.
- Individual and global configuration options (e.g., delays, thresholds).
- Month-specific thresholds for brightness and diffuse light conditions.
Management GUI
- Status display of groups and zones.
- Switch between manual and automated control modes.
- Access to weather data and log information.
Data Management and System Analysis
Logging of system messages and user actions.
Event logging for detailed error analysis.
Validation of imported data and error logging.
Backups through database copying.
User Roles
Role-based access control (e.g., Administrator, Manager, Viewer).
Different permissions for configuration, logs, and project data
Hardware Integration
Connection via KNX group addresses or IP addresses of KNXnet/IP routers.